Whether you own a CNC manufacturing company or are an investor in these CNC machining services, it is critical to understand the stages involved in processing CNC machining projects.
Several phases assist complete CNC machining tasks, from preparing materials to processing them, programming the CNC machine, monitoring production quality, and controlling the final finishing of the product or project. This in-depth essay will go over the procedures for processing CNC machining projects.

5-Step Guide for Processing CNC Machining Projects:
Material Preparation:
Material preparation for a CNC machining job is critical to ensure the finished product matches the needed parameters. Here’s a step-by-step guide on preparing material for a CNC machining project:
Choose the appropriate material
The first stage in preparing material for a CNC machining project is to select the appropriate material. The material should be both machinable with ease and durable enough to endure the forces applied during machining.
Cut the material to size as follows
After you’ve decided on the proper material, the next step is to trim it to size. This can be accomplished with saws, shears, and laser cutters. It is critical to be accurate when cutting the material, as any mistakes at this step can impact the final product.
Deburr the edges
It is critical to deburr the edges after cutting the material to size. This entails eliminating any rough edges or burrs from the cutting procedure. This can be accomplished using various equipment, including sandpaper, files, and deburring tools.
Clean the material
It must be completely cleaned when cut and deburred. This will aid in removing any dirt, grease, or other pollutants that may interfere with the machining process. To clean the material, you can use several cleaning chemicals, such as solvents and degreasers.
Clamp the material
Once the material has been cleaned, it must be securely clamped to the CNC machine’s work surface. This ensures that the material remains in place during the machining process and that the result is precise.
Prepare the cutting tools
Lastly, they must be programmed into the CNC machine. This includes choosing the appropriate cutting tool for the operation, determining the suitable feed rate and depth of cut, and ensuring that the cutting tool is properly aligned with the material.
Also Read: The Most Suitable Metal Materials for your CNC Machined Parts
Understanding and Using CAD/CAM Programming
CNC machining projects require AD (AutoCAD) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) programming software. AD produces 2D and 3D designs, whereas CAM creates tool paths that guide the CNC machine through cutting and shaping the material.
To begin this programming work, you must develop a design in AutoCAD. This entails drawing the desired part or component with various tools and techniques. When the design is finished, it can be saved in various formats, including DXF and DWG.
The design is then imported into CAM software. This entails launching the CAM software and selecting the design’s file format. After that, the CAM program will read the file and create a 3D model of the part or component.
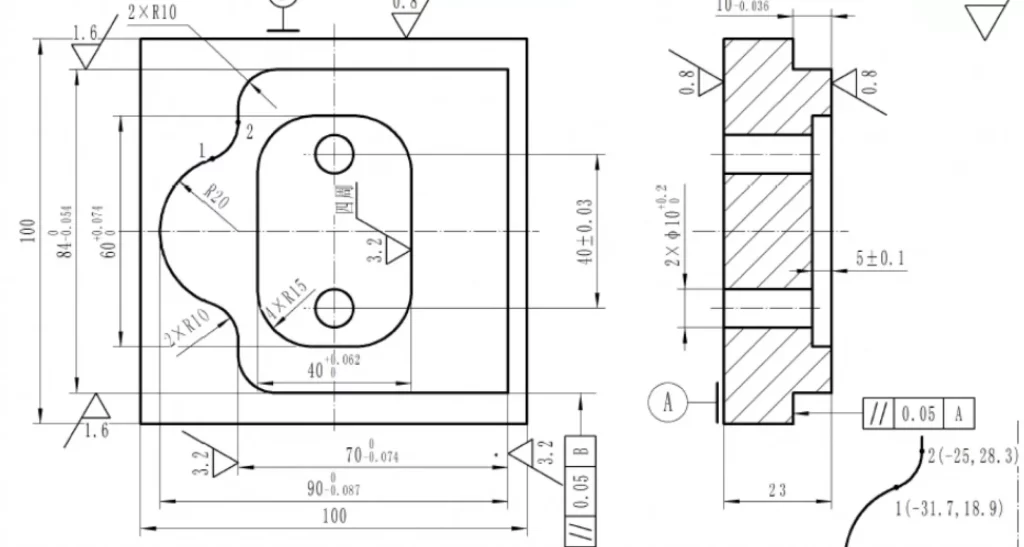
The tool paths are created once the 3D model has been constructed. Both must select the appropriate cutting tools and determine the path the tools will take to cut and shape the material. The CAM program will generate a G-code file with machining instructions for the CNC machine.
Following that, you must configure the CNC machine: Once the G-code file has been generated, the subsequent task involves configuring the CNC machine. Loading the G-code file onto the machine and selecting the right cutting tools are also required. The equipment must also be calibrated to ensure optimum material alignment.
Once the system has been configured, it is time to start the software. This entails starting the machine and monitoring the machining process to verify that the material is appropriately chopped and formed. Any errors or issues that develop during the machining process must be handled immediately to avoid damaging the material or the machine.
Machining Procedure
The primary machining process is another critical phase in CNC Machining projects. The material must first be loaded onto the CNC machine in this operation. This entails clamping the material to the work table or vice of the machine. The material must be appropriately positioned to ensure that it is aligned with the machine’s cutting tools.
After you’ve loaded the materials, it’s time to configure the CNC machine’s cutting tools. This entails selecting the proper tools and attaching them to the machine’s spindle. The cutting tools must be properly aligned with the material to ensure accurate cuts and forms.
The application is then run after the material and cutting instruments have been set up. This entails loading the G-code file developed during the programming process into the computer system of the CNC machine. The machine will then cut and shape the material according to the instructions in the G-code file.
You can better watch the machining process once the application is underway. While watching, ensure the material is appropriately cut and formed. This includes inspecting the cutting tools for wear or damage and monitoring the machine’s movements to verify that the material is cut appropriately.
Inspection and Quality Control
The next step in CNC machining project processing is inspection and quality control. In this process, you must develop a quality control strategy before beginning the machining process. This plan should detail the procedures that will be done to guarantee that the finished product fulfills the requirements and standards.
Once you have a plan, you can use measuring devices such as calipers, micrometers, and gauges during the machining process to determine the product’s dimensions. These measurements are compared to the appropriate requirements to verify that the product is machined precisely.

Now make sure to inspect the product at each stage. It will help you guarantee that the product is correctly machined. This includes visually assessing the product for faults or issues and checking the dimensions and tolerances with measurement devices.
Once you ensure no issues during the inspection, use SPC to continuously monitor the machining process. This tool will help you discover trends or patterns that may signal a problem. In this way, you can aid in defect prevention and ensure that the final product fulfills the criteria.
Afterward, it’s time to inspect the final product to ensure it fulfills the requirements and standards. This process entails inspecting the product’s size, surface finish, and other critical features with measuring devices and visual inspection.
In the end, you should record and documents the results of each inspection and quality control stage throughout the machining process. These records will help you track how certain problems can be solved during the processing of CNC machining projects, allowing you to detect and solve them easily in the future too.
Finishing Operations
Finally, finishing is critical in CNC machining projects because it ensures the product has the desired surface polish and looks. Following are some things to undertake at the finishing step of a CNC machining project:
Burrs and sharp edges should be removed: Burrs and sharp edges left on the product by the machining process can be harmful and hinder the product’s performance. These burrs and sharp edges should be removed during finishing with deburring tools or other means.
Smooth the surface finish: Depending on the project’s needs, the product’s surface finish may need to be smoothed to improve its appearance or performance. This can be accomplished with abrasive materials like sandpaper or polishing chemicals.
Coatings or finishes: Depending on the product’s application, coatings or finishes may be required to protect it from corrosion or wear. Anodizing, powder coating, and painting are common coatings utilized in CNC machining applications.

Examine the finished product: Once the finishing process is finished, the product should be inspected to ensure it satisfies the needed requirements and standards. This entails inspecting the product’s size, surface finish, and other critical features with measuring devices and visual inspection.
Product packaging: Following final product inspection and approval, it should be carefully wrapped to preserve it throughout shipping and handling. This may entail using protective packing materials such as foam or bubble wrap and labeling the package with pertinent information such as component numbers or client information.
Also Read: What Skills a Good CNC Machinist Should Have
Conclusions:
CNC machining projects undergo several procedures to be completed while maintaining quality, precision, and fine finishing. This article will help you comprehend and carry out these processes correctly.










