The beauty of plastic injection molding is that you may choose from various materials, each with advantages and disadvantages. Polyamide, better known by its brand name, Nylon, is one such plastic material frequently used in injection molding.
This thermoplastic’s outstanding blend of electrical and mechanical qualities makes it a great choice for applications in various fields. Let’s dive deeper into thermoplastic polyamide injection molding to help you better understand your possibilities.
Understanding Polyamide:
PA is an abbreviation for polyamide, often known as Nylon. It is a very important thermoplastics class for high-performance engineering applications. It features characteristics that are well-balanced overall. They have repeated amide connections, denoted by the notation -CO-NH. Condensation of copolymers with identical units and copolymers with differing units gives rise to its formation.
Wallace Hume Carothers was the one who first found Nylon. A chemist that DuPont de Nemours engaged in 1928 to lead an ambitious research program on the design of new polymeric materials. In 1935, he came up with the formula that would later become known as PA 66. This formula can be seen in the fig below.
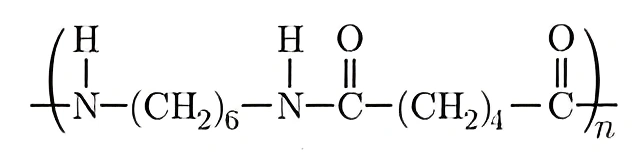
Physical and chemical properties of PA materials
Polyamides have a high temperature and a high resistance to electrical current. They also exhibit great resistance to chemical reactions thanks to the crystalline structure of their bodies. They have excellent properties in terms of both mechanics and barriers.
These materials are very amenable to the process of flame retardation. Polyamides were the first fibers to be commercially produced that could be considered fully synthetic.
Their stiffness can be brought up to par with that of metals when they are reinforced with glass fibers. There is a range of lengths possible for these glass fibers. For this reason, polyamides are frequently evaluated for use in projects that include metal substitution.

Suggested: 11 Widely Used Products Made by Injection Molding Today
Because amides are a chemical group, polyamides generally tend to absorb moisture. The moisture has a plasticizing effect on the substance. As a result, the tensile modulus decreases while the impact resistance and flexibility increase. Additionally, dimensional changes are tremendously impacted by the uptake of moisture.
When designing the parts, this factor needs to be taken into consideration. Today, polyamides have a variety of applications, including the automotive and transportation industries, the electrical and electronics industries, and consumer product manufacturing. We will also discuss these applications in this article.
Polyamide 6 and Polyamide 66:
As a common type of thermoplastic used in the manufacturing of various products, polyamide is divided into multiple sub-types of products, including:
- Polyamide 6
- Polyamide 12
- Polyamide 66
- Polyamide 69
- Polyamide 6-10
- Polyamide 6-12
- Polyamide 46
- Polyamide 1212
Now among these vast categories of polyamide, only two are commonly used for polyamide injection molding or PA injection molding process – Polyamide 6 and Polyamide 66.
The Similarities:
As mentioned above, PA6 and PA66 are the most commonly utilized polyamides worldwide. Because of their high performance/cost ratios, they are used in a wide range of applications. Their essential characteristics are:
- High-Temperature Strength and Stiffness: PA6 and PA66 have good mechanical strength and stiffness even at high temperatures, making them ideal for structural applications in automotive and industrial contexts.
- High Impact Strength, Even at Low Temperature: Both polyamides have high impact resistance, making them ideal for items subjected to dynamic stresses, such as protective gear and impact-resistant parts.
- Excellent Flow for Simple Processing: The outstanding flowability of PA6 and PA66 during PA injection molding guarantees the smooth and efficient production of elaborate patterns and complex geometries.
- Excellent Abrasion and Wear Resistance: These polyamides are suited for bearing, gear, and conveyor applications due to their high abrasion and wear resistance.
- Excellent Resistance to Fuel and Oil: PA6 and PA66 resist fuel and oil, making them useful in the automotive and aircraft industries.
- Great Fatigue Resistance: Both polyamides have high fatigue resistance, which ensures endurance under cyclic loads.
- Strong Electrical Insulating Properties: These polyamides are good insulators and can be used in electrical and electronic applications.
- High Water Absorption and Limited Dimensional Stability: PA6 and PA66 absorb much water, affecting dimensional stability in humid situations.
- Strong Mineral Acids and Polar Solvents Susceptible: Both polyamides are sensitive to strong acids and tend to absorb polar liquids.
- Dries Thoroughly Before Processing: To eliminate absorbed moisture, thorough drying is required before processing PA6 and PA66.
Also Read: CNC Milling Parts: What Factors Can Cause The Deformation?

The Differences:
Other than having some key properties that make both polyamide six and polyamide 66 ideal thermoplastics for production needs, some unique properties set both these types of polyamide apart. These unique properties can be seen in the table below:
| PA6 | PA66 |
| 1. Temperature resistance is slightly lower. 2. A little less expansive 3. Improved long-term heat aging 4. The superior appearance of the surface 5. Improved hydrolytic stability 6. Improved processability 7. Stiffness is comparable at temperatures below 180°C. 8. Low cost and temperature deflection | 1. A slightly lower ability to absorb moisture 2. Greater modulus 3. Improved heat resistance in the short term 4. Improved wear resistance |
Processing Conditions of PA6 and PA66 in Polyamide Injection Molding
When it comes to processing PA6 and PA66 in polyamide injection molding, a few critical factors need to be considered to achieve the best possible outcomes. It is strongly advised that the components be dried before they are processed, with a maximum moisture content of 0.2% being the target. The drying process is vital for preventing moisture-related issues and maintaining the desired qualities in the material.
Thermal Stability and Decomposition:
Polyamide 6 and Polyamide 66 are well-known for their remarkable thermal stability, as they can tolerate temperatures up to 310 degrees Celsius without decomposition. However, it is of the utmost importance to keep processing temperatures below this threshold, as temperatures greater than this can cause the substance to decompose.
The breakdown of PA6 injection molding and PA66 injection molding results in the production of carbon monoxide, ammonia, and caprolactam, all of which have the potential to hurt the quality and functionality of the finished product.
Suggested: Thermoforming vs. Injection Molding – Which is Better?
Polyamide Injection Molding Considerations:
L/D Ratio:
The length-to-diameter (L/D) ratio of the screw on the injection molding machine should ideally fall somewhere between 18:22 for the most effective PA6 injection molding and PA66 injection molding.
This guarantees that the polymer melt is properly mixed, melted, and homogenized, all of which contribute to producing high-quality molded parts.
Melt Temperature:
During the PA injection molding process, the temperature of the melt is a significant parameter. The ideal range for the melt temperature of PA6 injection molding is normally between 240 and 270 degrees Celsius, but the melt temperature of PA66 should be kept between 270 and 300 degrees Celsius.
It is crucial to control the melt’s temperature well enough to get the right flow properties and avoid problems like thermal degradation and material degradation.
Mold Temperature:
Keeping the mold at the correct temperature is equally important for successful polyamide injection molding. The mold temperature should be between 55 and 80 degrees Celsius for PA6 injection molding and PA66 injection molding, which is the acceptable temperature range.
The controlled temperature of the mold contributes to attaining a good surface finish, accurate dimensions, and high overall part quality.

Common Applications of Polyamide:
Because of its one-of-a-kind properties, polyamide is a material of choice in various industries, ranging from automobile components to food containers and textiles. The following is a list of typical applications for polyamide:
● The Gears, Bearings, and Bushings Market in the Automotive Industry
Because of its low-friction qualities and strong resistance to wear, polyamide is an excellent material for manufacturing gears, bearings, and bushings for use in the automotive industry.
The ability of polyamide to survive such conditions provides smooth functioning and a long mold lifespan in automotive applications. These components are constantly exposed to friction and mechanical stress, and because of this, polyamide is used.
● Polyamide Products Manufactured in Food and Hygiene Industries:
Because of its malleability and non-toxic nature, polyamide is a material that is highly sought after in the food and hygiene industries. It is frequently used to produce toothbrushes, holders, and cookware.
Because of its capacity to withstand high temperatures without losing its structural integrity, polyamide is an excellent material for manufacturing food containers and cookware. This allows for the safe storage and preparation of food. Also, because it is non-toxic, brushing your teeth with a polyamide toothbrush is safe.
● Garments & Fabrics Made of Nylon
In addition to its use in PA injection molding, polyamide is widely recognized for its presence in the fashion sector through Nylon fabricating fabrics and clothes.
Clothing and athletic wear manufacturers develop high-quality clothes resistant to wear and tear by weaving together polyamide threads. Due to the high abrasion resistance that nylon clothing provides, it is a good choice for use in both active and outdoor settings.
Advantages and Factors to Consider
Polyamide is a flexible material that can be utilized in various contexts because of its exceptional combination of qualities, including resistance to heat and chemicals and a high degree of flexibility. It is known for being a sturdy thermoplastic that can be used in various industries because of its resistance to wear and tear and its capacity to survive extreme environments.
However, it is vital to consider various issues connected with polyamide, such as its ability to absorb moisture and its susceptibility to ultraviolet (UV) light. These challenges may require proper design and processing considerations to be made.
Conclusion:
When working with PA6 and PA66 in polyamide injection molding, adhering to suitable processing parameters is critical. Manufacturers may produce high-quality, durable, and reliable products across various sectors by adhering to specified drying techniques and maintaining optimum melt and mold temperatures.
If you still have queries, contact our professional manufacturers at Prototool.











