If you’re new to the world of Spritzgießen in the production industry, the term ‘sprue bushing’ may confuse you. Simply put, it’s a component used in injection molding machines that plays a vital role in production.
But there’s more to exploring how sprue bushing works and what should be considered to ensure the best production returns while using sprue bushing. Are you curious about these details? Then let’s go ahead and learn all about sprue bushing, shall we?
What is a Sprue Bushing?
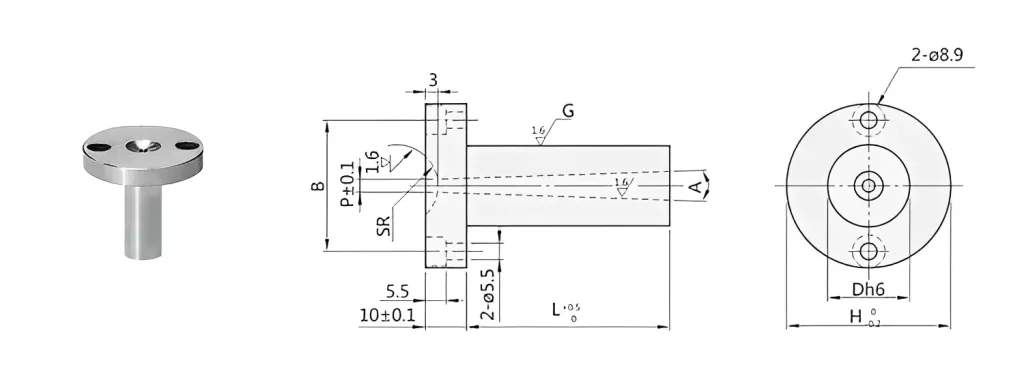
Sprue Bushings are an internal sprue component. They’re made of hardened steel and aid in accepting an extrusion nozzle. Sprue bushings offer the necessary opening for the molten plastic to be transferred into its respective mold cavity. These components contribute to a more rigid sprue and shorter cooling periods. Sprues must be sturdy because pickers and other industrial robots pick up molded pieces when ready for removal.
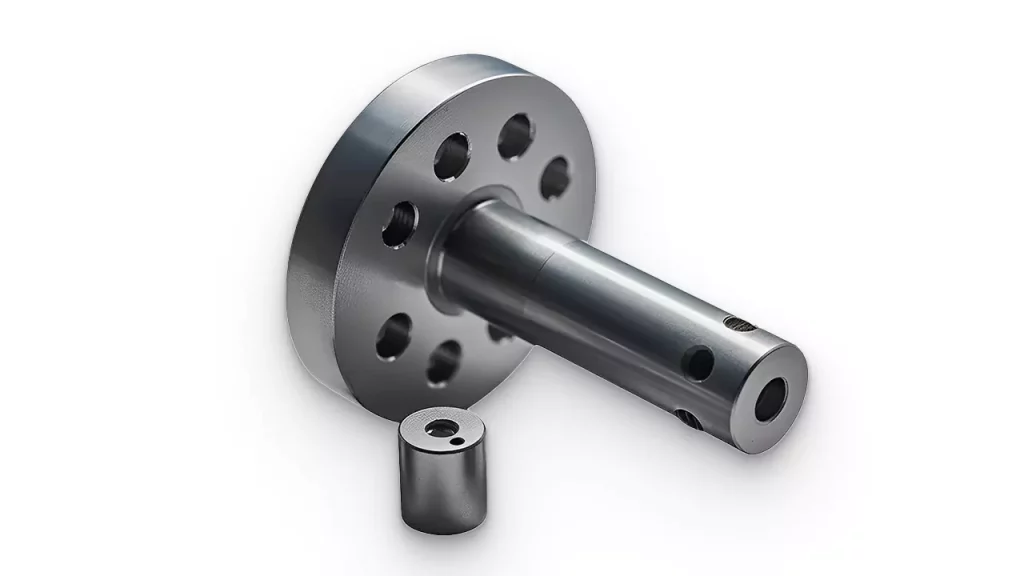

Sprue bushings are shaped and sized similarly to bolts. Because they are intended to aid in the attachment of the sprue, they are secured with two bolts to ensure that the sprue does not separate during periods of high injection pressure. Sprue bushings are made of hot working steel SKD61 and have heat and wear resistance qualities.
Sprue bushings are often constructed of hardened steel or a copper-based alloy. In some circumstances, they may be lined with carbide to help with wear and corrosion resistance and faster heat transmission rates. Carbide-lined sprue bushings can be extremely useful when working with abrasive resins.
Their primary role is to prevent plastic material leakage during the injection mold process. To accomplish this, we must size the sprue bushings properly to work with the feed throat. Typically, the feed throat is built as a chamfer R. The mold sprue’s spherical radius, or SR, must be one to two millimeters bigger than the injection nozzle’s spherical radius.
Lesen Sie auch: Erkennen und Korrigieren von Kurzschlüssen - ein häufiges Problem beim Spritzgießen
Wie funktioniert es?
When the process of injection molding first begins, the plastic material that will be used is pumped into the sprue bushing. From there, it moves through the runners, which are channels that transport the molten plastic to various spots within the mold. Once it reaches the end of those channels, the mold is complete. The runners ultimately lead to the gates, which are small apertures that route the plastic material into the mold cavities where the final product is made. The gates are located at the end of the runner system.
The sprue bushing is essential, as it helps ensure that the mold cavities are filled effectively and uniformly. It helps manage the flow rate and pressure of the molten plastic, preventing difficulties like air pockets and partial filling by ensuring that the proper pressure is maintained. In addition, sprue bushings have the potential to be developed with other characteristics, such as temperature control, that are intended to assist in the upkeep of ideal processing conditions.
During the mold opening process, the sprue and runner system and the sprue bushing are normally separated from the final product and removed before the mold is opened. This occurs after the plastic material has cooled and set inside the mold. Because of this, the product can be extracted from the mold in a pristine state.
In conclusion, a sprue bushing is a component used in injection molding and serves as a conduit for the liquid plastic to enter the mold cavity. This component is also known as a sprue bushing. It is an important part of the injection molding process and helps guarantee that the mold is properly filled with the material.
The Types of Sprue Bushing:
There are two common types of sprue bushing used in injection molding. These types include:
● Cold Sprue Bushing:
A cold sprue bushing is not heated and produces a sprue that must be removed during a secondary operation. This bushing type is inserted into a mold and aids in forming a channel between the molding machine nozzle and the mold chamber. The spherical radius and the O-shaped hole opening are the two most essential nozzle dimensions of the cold sprue bushing.
● Hot Sprue Bushing:
Like a cold sprue bushing, a hot sprue bushing is placed into the mold. However, these sprue bushings offer a hot path between the mold chamber and the mold nozzle. Furthermore, a heating element housed within the bushing assists in keeping the melted resin or plastic hot as it travels through it.

Design and Operation:
Sprue bushings normally have a spherical radius of .50″ or.75″ flat-type bushings with a flat surface rather than a nozzle radius are also available. Buyers must also specify several other dimensions, including:
● The Length of the Shank:
Start measuring the shank length from the sprue bushing head’s underside to the bushing’s end. Like the overall length measurement, this dimension does not include the nozzle.
● The Diameter of the Tip Hold:
The diameter of the entrance hole on the nozzle seat is described by the tip hold diameter, also known as the “O” diameter. This measurement is also known as the ‘gate diameter’ or potentially the melt passage diameter.’ This measurement, by whatever name it is known, is effectively the hold that connects the nozzle tip to where the material enters the sprue bushing.
● The Total Length:
When measuring the overall length of the sprue bushing, measure it from the beginning to the end, excluding the nozzle measurement.
Lesen Sie auch: Die Bedeutung von Design und Position des Angusses beim Spritzgießen
Common Issues That Occur in Sprue Bushing:
Knowing what could go wrong with sprue bushings and the kinds of problems they could create is a crucial component of comprehending the function of these components.
It is essential to know how to identify and fix sprue bushing issues on the production floor to avoid processing problems and improve cycle times, two key goals for any production process. Because of this, it is important to know how to detect and resolve sprue bushing issues.
Surface Finish Issues:
Be on the lookout for rust, scratches, pitting, and other machine markings when inspecting your sprue bushing. If any of these irregularities are present in the bore of the sprue bushing, the sprue may become obstructed in the bushing. Although pitting brought on by corrosive or abrasive materials could be to blame, most of these situations are brought on by either human mistakes or improper machine maintenance.
When someone tries to remove a sprue lodged within a bushing, this common situation leads to internal scratches and rolled edges.
The conventional approach, which consists of using a brass rod to force the sprue out from the nozzle seat side, can potentially present a problem because it is difficult to manipulate the rod in that position.
In this instance, the issue can be remedied by heating a brass screw with propane or a MAP gas torch and then putting it into the sprue through the mold’s parting line. This should bring about the desired result.
A pair of brass pliers can pry out the sprue once it has cooled down to the appropriate temperature. Because sprues can be quite pricey, it is recommended that you avoid using instruments made of hardened steel, such as screws, screwdrivers, various kinds of pliers, and gate cutters.
Shrinking Issues:
Molded sprues need to reduce some of their taper lock in the bushing by allowing them to shrink slightly. The sort of material it is manufactured with, and the degree to which it is packed out tightly directly affects how well it shrinks.
If you are not utilizing a molding material with a shallow Schrumpfung factor, achieving the appropriate amount of shrinkage should not be a problem for you. Amorphous materials that are densely laden with filler and liquid-crystal polymers, or LCPs, are two types of materials that can fall under this category.
On the other hand, shrinkage can become a problem when molding packs too much material onto the sprue and prevents it from shrinking appropriately. When the packing pressure remains for a significant amount of time after the gates have frozen, this is something that frequently occurs.
In addition, the sprue can become overpacked if the sprue orifice is still liquid during a hasty sprue recovery or if high back pressure is used to incorporate a colorant. In contrast, the sprue is being recovered, which can cause the sprue to be overpacked.
Another circumstance that can result in gradual shrinkage is one in which the bushing of the mold does not receive sufficient cooling even though the cycle period is rather quick.
Nozzle Seat Issue
At the beginning of each process, it is essential to visually inspect the sprue bushing nozzle. During this inspection, the workers should search for any signs of probable malfunction, such as rolled edges, chips, cracks, burrs, dents, plastic, residue buildup, etc.
After each manufacturing run, the nozzle seat should also be examined for quality assurance. When this is done, it is easier to determine whether the part must be fixed while the mold is still available.
Regarding nozzle seat repairs, the two ways that are utilized most frequently are refacing tools and carbide cutters. Before employing carbide cutters for the first time, it is necessary to check the radius of the cutting edge.
Although cutters are not always built with the appropriate tolerance, it is essential to check that the dimension of the sprue bushing nozzle seat radius is accurate to avoid problems. When machining the sprue bushing seats, using a rotary EDM can help reduce the risk of molten plastic escaping or carriage blowback.
Utilizing a stipple finish is another good method for ensuring that any future damage will be quickly spotted and repaired.
Schlussfolgerung:
Sprue bushings are indispensable in manufacturing by facilitating the flow of molten materials from the injection hose to the mold cavity. Even though they are just one component of a larger machine, they need careful monitoring and competent servicing.
Therefore, it is crucial to ensure the success of the manufacturing process to have a thorough awareness of the numerous components and aspects that contribute to their proper performance.
Have more questions about Angussbuchse? Fragen Sie unsere Experten unter Prototool.de.










