You’re probably already considering potential production methods for your project. So, which production method is best? 3D printing vs. injection molding, and why?
With this detailed guide, we will help you choose between moldagem por injeção e Impressão 3D to give life to your project by comparing and contrasting the two processes and highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses.
Making the Right Manufacturing Choice:
Among 3d printing and injection molding, both are excellent manufacturing procedures but are very distinct and can aid in completing diverse projects. This is entirely dependent on your requirements. Even if injection molding appears to be more professional, things are changing, and 3D printing is becoming a viable alternative, allowing for the creation of extremely exact parts.
These two strategies can help you with your rapid prototyping and production processes. They both have advantages, but which one will benefit your manufacturing process? To do so, you must first understand what these processes are.
Definition:
- Moldagem por injeção:
Injection molding, a common industrial method used for decades, involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity to create a product. In this manufacturing process, people inject the molten material into the mold, solidifying as it cools and shaping the goods.
- 3D printing:
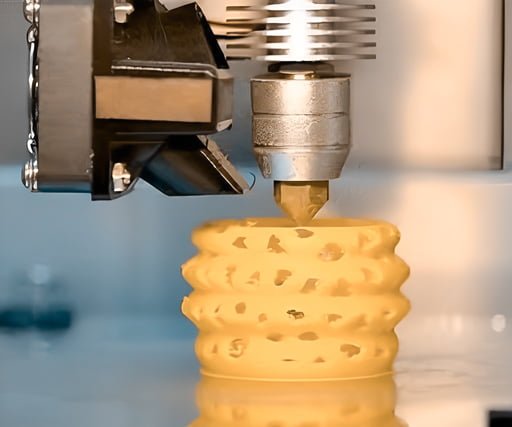
On the other hand, additive manufacturing, which is what 3D printing is, involves building up an object layer by layer. With this method, a 3D file is required to start the manufacturing process; a mold is unnecessary. These days, you can get your hands on a wide variety of 3D printing technology and materials.
The Benefits:
- Injection Molding Advantages
When it comes to high-volume manufacturing, injection molding has many advantages. The process is streamlined due to its precision and repeatability. Injection molding allows you to make things with a wide variety of qualities since you may use a wide variety of materials, from plastic to metals.
Injection molding is particularly useful for manufacturing on a large scale. This method is ideal for making a product with complicated contours and ornamentation. You can tailor a part’s strength, flexibility, or other physical attributes to its intended application by selecting the appropriate material from among the many available options.

- 3D Printing Advantages
When comparing additive manufacturing to more conventional methods like injection molding, its many advantages become clear. In the first place, it works better with iterative designs, so if your project is still a work in progress, this method is for you.
For a long time, prototipagem rápida was seen as the ideal use for 3D printing. But that’s no longer the case, and it hasn’t been for some time because technology has improved and become more trustworthy. Despite this, prototyping is one of its strong points because it can do it rapidly and with less waste than other techniques.
Before printing again, you can test your idea with a simple printout and make any necessary adjustments in the 3D modeling software. Then you may print it out and double-check your work before submitting it for publication. As you refine your product’s design, this adaptability will save you both time and money.
With 3D printing, almost no materials go to waste. All you need to use is the number of materials necessary for the task. This is a significant plus compared to conventional manufacturing techniques like computer numerical control (CNC) machining and injection molding.
If you can print your design on demand, you can avoid having any extra materials on hand, which can add to the cost. Printing finished goods on demand eliminates the need for warehousing or supply chain management since it eliminates these issues.

The Difference:
Regarding whether the manufacturing process is superior, injection molding and three-dimensional printing each have compelling arguments in their favor. Nevertheless, it all depends on the requirements that you have in mind. Both methods of 3d printing vs. injection molding come with unique advantages and favorable characteristics. It includes:
- Cost Difference:
Injection molding methods often need expensive machinery, with some machines reaching prices in the hundreds of thousands of dollars. On the other hand, investing in one of superior quality can provide you with years or even decades of service.
Those who are self-employed or developing their goods may find that purchasing one is not the most productive use of their financial resources. It is not something that you would want to buy for yourself. Nevertheless, there is a solution that is available that is more economical, and that is to hire service providers who specialize in injection molding.
The fact that you require molds specifically made for your product is another factor contributing to the high cost. This could add several thousand dollars or tens of thousands of dollars to the total cost.
Printing three-dimensional objects with a 3D printer is much more affordable than injection molding. Firstly, the printer is far more affordable. You have a wide variety of possibilities to pick from, so regardless of whether you work in production or as a hobbyist, you should have no trouble locating the most suitable product to meet your requirements and complete your projects. The cost of a 3D printer is often in the thousands of dollars, but there are no additional upfront fees because there is no need to construct a bespoke mold.
Similarly, several businesses now provide 3D printing services in addition to injection molding. This method is even more economical, as the only costs incurred are those associated with the usage of the machine and the ingredients. On the other hand, the new printers that are being produced right now make it possible for even the smallest industrial companies to get their own devices.
- Timing Difference:
When it comes to the duration it takes to complete one product cycle of 3d printing and injection molding, injection molding is the procedure that takes the least amount of time. However, this isn’t all to the process because developing, manufacturing, and perfecting molds can take significant time.
A bespoke mold from steel or aluminum can take weeks to months. If you rely on a service provider, they may require you to wait for the allocated machine time. Because of these several considerations, the turnaround time will be significantly greater than it would normally be. However, once everything is organized, performing your role should not take too much time.
The process of 3D printing does not require any kind of lead time. You are prepared to move forward once the design has been completed using the software you have. Printing your component will take some time; in most cases, it will take a few hours.
- Volume Difference:
The manufacturing volume is the primary area where injection molding and 3D printing diverge significantly. Injection molding is still the method of choice for high-volume production, even though three-dimensional printing saves a significant amount of money on the equipment and the materials used.
Injection molding is the technique you should use to produce batches of tens of thousands of pieces or more at a time or higher. At these high production rates, your financial investment in producing the ideal mold and purchasing a machine ought to pay for itself and then some.
On the other hand, 3D printing is an excellent option for low to medium-volume requirements. The most compelling examples in this category are prototyping and production on demand. This is the most effective approach when looking for a method of prototyping that is easy on the wallet.
You may also reduce your costs by reducing your storage amount because you can print just when needed. The 3D printing technology has also advanced to the point where it can generate your models reasonably, making it possible to manufacture runs to number in the thousands.
How to Use Them? 3D Printing vs. Injection Molding:
Moldagem por injeção:
You cannot use this technology without the usage of specific equipment. To employ injection molding, specific specialist machines are required. A material hopper, an injection ram, and a heating unit are all part of these injection molding machines.
Making molds for your injection molding method is an expensive operation that limits your prototyping options: Molds can be fairly expensive to recreate each time you need to make numerous iterations. Because these molds are often composed of steel, making adjustments is difficult and cannot be suited to your prototype development.
However, it is a viable option if you intend to create huge quantities. Remember that this process still has high injection molding tooling costs and a lengthy necessary turnaround time.
3D printing:
In terms of application, 3D printing differs from injection molding. There are numerous applications for additive manufacturing. If you require a 3D printing filament, you can purchase a 3D printer, such as an FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling). Your firm can purchase larger and more professional 3D printers, such as SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) 3D printers. However, purchasing your industrial 3D printer may be an expensive investment for your company, and it may not be worth it.
Alternatively, you may use a 3D printing service provider like Prototool. 3D printing technologies used by these service providers will assist you in creating all of your best ideas, from metal to plastic and resin. When hiring professional companies to offer you the service, you can choose from several technologies, such as Multi Jet Fusion, CLIP (DLS), DMLS, and 3D Printing.
Conclusão:
Ultimately, your requirements will fully determine the process/technology you choose for 3d printing vs. injection molding. Both have their own set of advantages, features, and outcomes. However, you may mix these two methods to get the most out of what they’re best at – it all depends on your production demands!










