The CNC lathe machine headstock plays a vital role in machining, serving as the powerhouse that drives rotation and securely holds the workpiece. A geared transmission that supplies power and rotation to various lathe components is known as a CNC lathe headstock.
Let’s explore the definition, design, and function of the CNC lathe headstock.
Sugerido: Tipos de máquinas CNC - Os tipos e como funcionam
What is a CNC Lathe Headstock?
The CNC lathe machine headstock is a vital and integral part of the overall machine structure. Positioned at the left end of the lathe bed, it serves as the central hub for the rotational movement of the workpiece during machining operations.
At the heart of the headstock lies the main spindle, which is responsible for generating the rotational motion required for viragem, drilling, and other machining processes. This main spindle is powered by the machine’s motor, which transmits torque and speed to achieve precise and controlled movement.
In addition to the main spindle, the headstock also houses the mechanism for securely holding the workpiece. This mechanism can take the form of a chuck or a collet, depending on the specific requirements of the machining task at hand.
These holding devices ensure the workpiece remains firmly positioned, allowing for accurate and consistent machining operations.
Function of a CNC Lathe Headstock:
The headstock’s primary function is to transmit power from the motor to the workpiece, enabling the necessary rotation and movement for machining. By securely gripping the workpiece and rotating it at varying speeds and directions, the headstock facilitates the creation of intricate shapes, contours, and features with precision and repeatability.
Furthermore, the headstock plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and accuracy of the machining process. Its robust construction and precise alignment ensure the workpiece remains firmly held, minimizing unwanted vibrations or deflections during machining.
This stability is essential for achieving high-quality surface finishes, tight tolerances, and dimensional accuracy in the final machined parts.
Overall, the CNC lathe headstock acts as the powerhouse of the machine, providing the necessary rotational motion and holding capabilities to execute a wide range of machining operations. Its reliability, precision, and stability are crucial for achieving consistent and efficient machining results.
By understanding the importance and function of the headstock, manufacturers can optimize their CNC lathe machining processes, enhance productivity, and deliver superior quality products to meet the demands of modern manufacturing.
Structure of a CNC Lathe Headstock:
The design of a CNC lathe headstock is critical to the machine’s functionality and performance. It encompasses several intricate components that work together seamlessly to provide rotational motion and secure the workpiece during machining operations.
At the heart of the headstock is the main spindle, a cylindrical component that serves as the powerhouse of the machine.
An electric motor is usually responsible for generating the necessary torque and speed to accomplish various machining tasks. The main spindle is engineered with precision to ensure smooth rotation and accurate positioning of the workpiece.
The headstock incorporates a chuck or collet mechanism to hold the workpiece securely. The chuck consists of jaws that grip the workpiece firmly, while a collet is a specialized holding device that contracts around the workpiece, ensuring a secure grip.
These mechanisms provide stability and prevent any unwanted movement during machining. Additionally, the headstock includes high-precision bearings to support the rotational motion of the main spindle.
These bearings minimize friction and enable smooth, precise rotation, contributing to the overall accuracy and durability of the machine.
Leia também: A importância do design e da localização do canal de entrada na moldagem por injeção
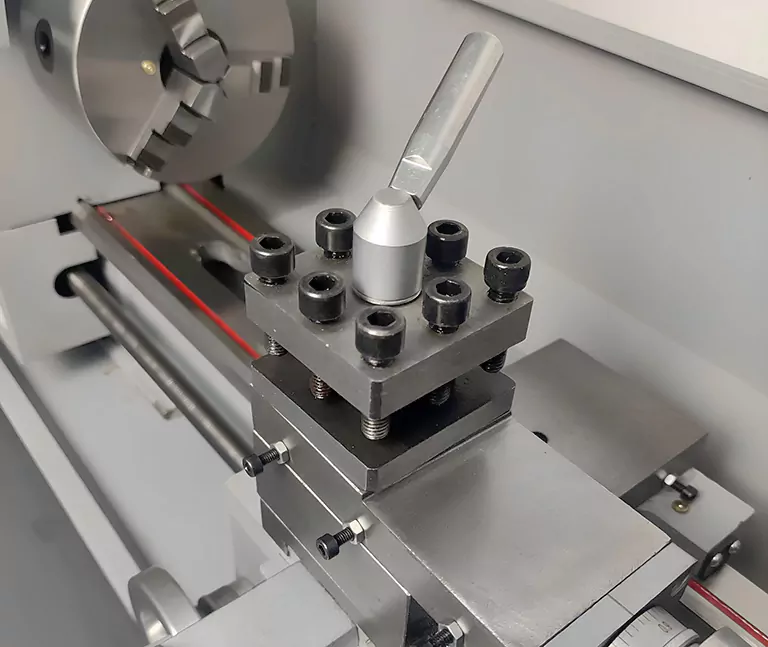


Applications of CNC Lathe Headstock:
The CNC lathe headstock is a versatile component with widespread application across various industries, including aeroespacial, automóvel, médico, and general manufacturing. Its capabilities enable a range of essential machining operations. Let’s explore some key uses in more detail:
1. Turning Operations:
The headstock is instrumental in the turning process, which involves shaping cylindrical workpieces. The headstock creates symmetrical shapes and contours by securely holding and rotating the workpiece. This functionality is invaluable for manufacturing shafts, bushings, and other rotational parts.
2. Drilling and Boring:
By incorporating drilling and boring tools, the headstock empowers the CNC lathe machine to create precise holes, threads, and bores in the workpiece. This capability facilitates the production of intricate designs, the assembly of components, and the incorporation of fasteners.
3. Tapping:
The headstock’s versatility extends to tapping operations, enabling the creation of threaded holes in the workpiece. By utilizing appropriate tooling, the headstock helps produce threads of various sizes and pitches, enhancing the functionality and versatility of the manufactured parts.
4. Milling and Grooving:
Utilizing milling cutters or grooving tools, the headstock opens doors to creating flat surfaces, slots, and grooves on the workpiece. This expands the design possibilities and allows for producing complex features, such as keyways, flutes, or intricate patterns.
5. Indexing and Multi-Axis Machining:
Advanced CNC lathe machines with programmable headstocks offer indexing and multi-axis machining capabilities. This sophisticated functionality allows for producing complex geometries, such as spirals, splines, or helical forms (Check fresagem helicoidal). By precisely controlling the movement and orientation of the workpiece, these machines can achieve intricate designs and meet intricate manufacturing requirements.
The versatility of the CNC lathe headstock is a boon for manufacturers across various industries. Its ability to perform turning, drilling, tapping, milling, grooving, and advanced indexing operations makes it an indispensable tool in modern machining processes.
By utilizing the capabilities of the headstock, manufacturers can produce intricate, accurate, and superior components, pushing the limits of innovation and satisfying the changing requirements of their industries.
Types of CNC Lathe Headstock:
Two types of CNC lathe headstocks are commonly used in the industry: fixed headstock and sliding headstock. Let’s explore each type in more detail:
Fixed Headstock:
The fixed headstock, also known as a box-type headstock, is a stationary component that houses the main spindle and other associated mechanisms. It remains fixed in its position throughout the machining process. The workpiece is clamped and secured in the chuck or collet, while the headstock provides rotational motion to the workpiece.
Moreover, fixed headstocks are typically found in standard CNC lathe machines and are well-suited for heavy-duty machining applications, larger workpieces, and high torque requirements. They offer excellent rigidity, stability, and consistent performance, making them ideal for operations that demand precision and accuracy.
Sliding Headstock:
The sliding headstock, also referred to as a Swiss-type or sliding headstock lathe, is a movable component that can slide along the lathe bed. Unlike the fixed headstock, the sliding headstock moves closer to the workpiece, allowing for more precise machining of smaller, intricate parts.
Sliding headstock lathes are commonly used in watchmaking, medical device manufacturing, and electronics industries, where high precision and intricate details are crucial. They excel in producing small, complex components with tight tolerances, as the proximity of the headstock to the workpiece enhances accuracy and reduces deflection during machining.
The choice between a fixed headstock and a sliding headstock depends on the specific requirements of the machining operation. Factors such as the size and complexity of the workpiece, required precision, and production volume play a significant role in determining the appropriate headstock type for a particular application.
It’s important to note that within each type, there can be variations and customizations to suit specific machining needs. CNC lathe manufacturers may offer different models and configurations of headstocks to meet the diverse requirements of their customers.
By understanding the differences between fixed and sliding headstocks, manufacturers can make informed decisions when selecting a CNC lathe machine that aligns with their specific machining goals and production requirements.
Leia também: 6 Desafios comuns enfrentados pelas empresas de fabrico CNC
Conclusão:
O CNC lathe headstock is a critical component in the machining process. Its proper functioning and regular maintenance are essential for achieving accurate and precise results, ensuring operator safety, and maximizing productivity. Manufacturers can appreciate its significance in their operations by understanding the headstock’s uses, applications, and importance.
Hence, it is crucial to establish a comprehensive maintenance plan to avoid the potential consequences of a damaged or unmaintained headstock. Regular inspections, lubrication, and timely repairs are essential to keep the headstock in optimal condition.
By investing in proper maintenance, manufacturers can enhance machining precision, minimize downtime, reduce costs, and uphold their reputation for delivering high-quality products.
Recognizing the CNC lathe headstock’s importance and prioritizing its maintenance is crucial for efficient and reliable machining in manufacturing.
For more details and queries, feel free to consult our professional CNC machining technicians at Prototool.com.
.










