Roughing Step In CNC Machining
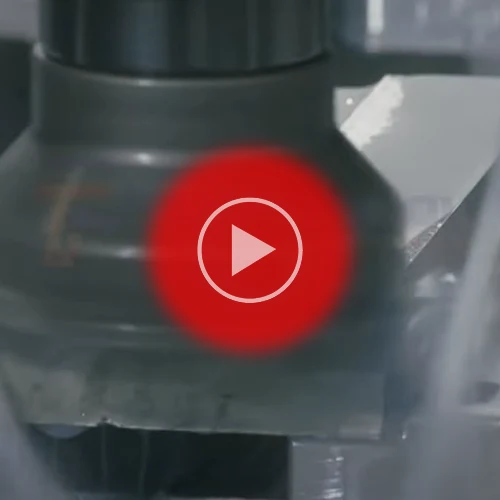

The rough machining step is an initial machining operation performed on a workpiece to remove excess material quickly and efficiently, typically leaving behind a rough surface finish.
On-Time CNC Parts Shipment And Transshipment

🚛🔧2.0X speed to view the Prototool’s on-time CNC parts shipment and transshipment process ~
High-Quality Car Parts Manufacturing with Haas 5-Axis Machining Technology

Using CNC machining for high-quality car parts is a well-established process today. Fast, precise, high-volume production, and cost-efficiency are the goals every factory strives for.
Top-Quality Aviation Parts Processing By CNC 5-axis Machine
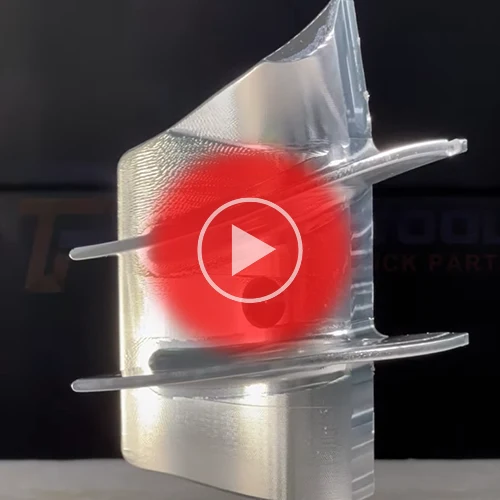
Aviation parts processing by CNC involves using computer-controlled machining techniques to manufacture precision components for aircraft, ensuring high quality, consistency, and adherence to strict aerospace standards.
Machining Delrin | Best Practices for Precision POM Machining
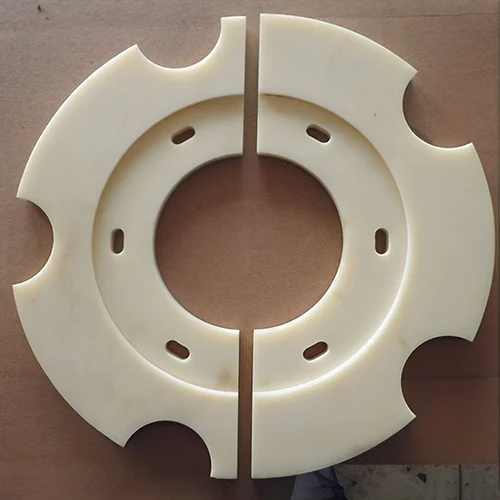

Gain a complete understanding of machining Delrin or POM materials through the experience shared by the major company Prototool.
ABS Machining | Challenges, Helpful Tips, Material Finishing Methods, & More!
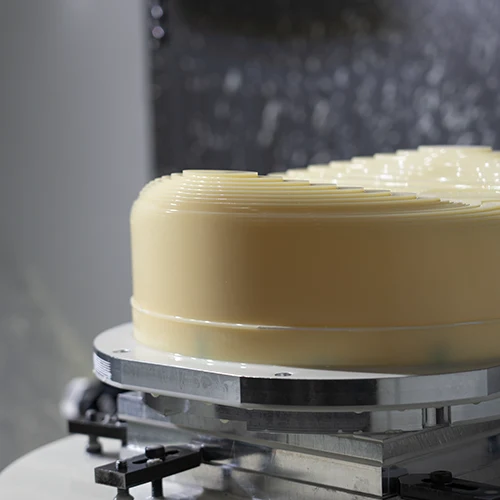

A professional ABS machining company shares information about the challenges of machining ABS and how to make top-quality plastic parts.
Tools, Techniques, Key Parameters And Surface Finishing Method For Steel Machining
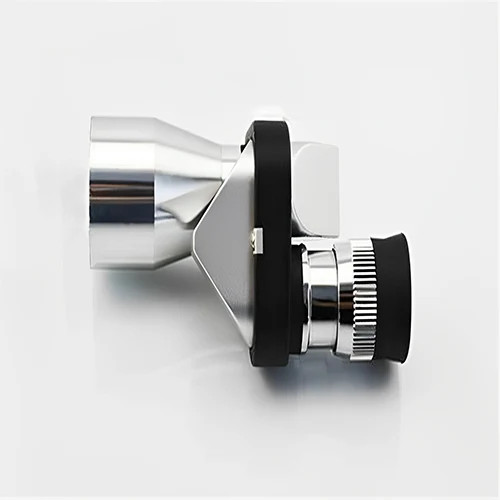

Prototool is a proficient metal machining company, with a special expertise in CNC steel machining, and we’ll share our advanced skills to you
Mill The Steel Block Into Metal Marvels
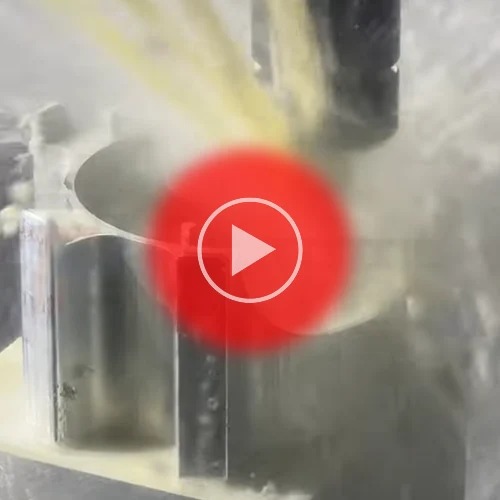

Typically, the processed metal is in block form; this makes it easier for CNC machining to create the desired shapes.
Prototool Uses Baofeng CNC Machine For Batch Processing Of Electrodes
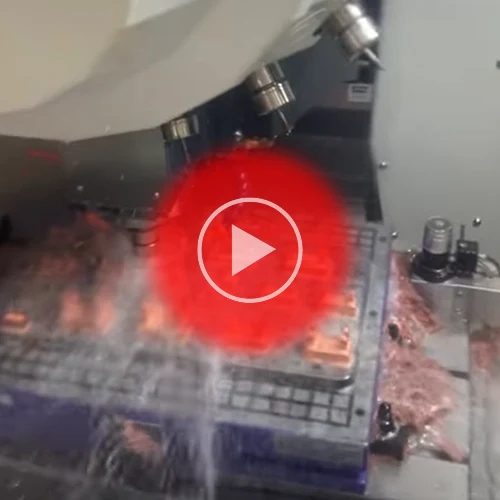

Prototool uses a large Baofeng CNC machine to batch process multiple copper electrodes for EDM by changing different types of cutting tools
Why Is Machining Coolant A Necessity In Machining?
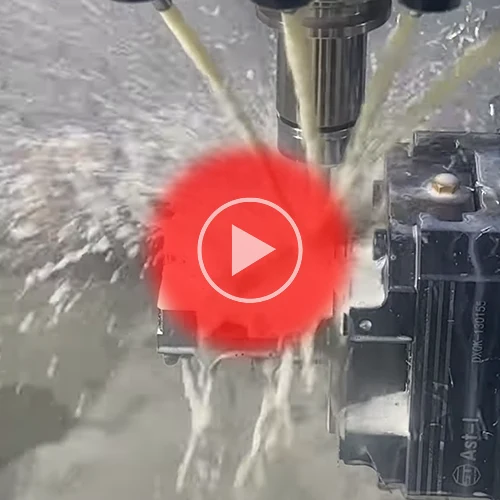
Machining coolant, or cutting fluid, is indispensable in machining because it serves multiple critical functions. It dissipates the heat generated during machining, preventing overheating of both the workpiece and the cutting tool. This heat dissipation also contributes to prolonged tool life and improved machining accuracy. Coolant acts as a lubricant, reducing friction between the tool […]
